Dua mol gas ideal monoatomik pada suhu - 73oC mempunyai energy dalam sebesar joule (Konstanta gas universal = 8,314 J/mol K) (A) 1662 (B) 2493 (C) 3342 (D) 4155 (E) 4986 9. Bila sejumlah gas yang massanya tetap memuai secara isotermis, maka molekul-molekul gas itu akan (A) Mempunyai energy kinetic lebih besar (B) Mempunyai momentum lenih. UN FISIKA 2019 tentang termodinamika 27, Suatu gas ideal monoatomik yang berada di dalam ruang tertutup mula-mula tekanannya 2 x 10 6 Pa dan volumenya 25 liter, kemudian menjalani proses isobarik sehingga volumenya berubah menjadi 10 liter. Gas lalu mengalami proses isokhorik sehingga tekanannya berubah menjadi 5 x 10 6 Pa, selanjutnya gas mengalami proses isotermik sehingga tekanan dan.
In physics and chemistry, 'monatomic' is a combination of the words 'mono' and 'atomic', and means 'single atom'. It is usually applied to gases: a monatomic gas is one in which atoms are not bound to each other. Examples at standard conditions include the noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon, though all chemical elements will be monatomic in the gas phase at sufficiently high temperatures. The thermodynamic behavior of a monatomic gas is extremely simple when compared to polyatomic gases because it is free of any rotational or vibrational energy.[1]
Update Google Chrome on Mac 10.7 Lion From the end user point of new, the update offers full-screen support on Mac OS X Lion which is a huge plus for power users. Also, Chrome is streamlined with Lion’s overlay scrollbars. The update also includes Web Audio API that lets developers to add special audio effects without leaving the browser. Question: Q: Google chrome and os x lion 10.7.5 More Less. This site contains user submitted content, comments and opinions and is for informational purposes only. Apple may provide or recommend responses as a possible solution based on the information provided; every potential issue may involve several factors not detailed in the. Chrome os x lion.
Noble gases[edit]

The only chemical elements that are stable single atommolecules at standard temperature and pressure (STP) are the noble gases. These are helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, and radon. Noble gases have a full outer valence shell making them rather non-reactive species.[2] While these elements have been described historically as completely inert, chemical compounds have been synthesized with all but neon and helium.[3]
When grouped together with the homonucleardiatomic gases such as nitrogen (N2), the noble gases are called 'elemental gases' or 'molecular gases' to distinguish them from molecules that are also chemical compounds.
Thermodynamic properties[edit]
The only possible motion of an atom in a monatomic gas is translation (electronic excitation is not important at room temperature). Thus by the equipartition theorem, the kinetic energy of a single atom of a monatomic gas at thermodynamic temperatureT is given by , where kb is Boltzmann's constant. One mole of atoms contains an Avogadro number () of atoms, so that the energy of one mole of atoms of a monoatomic gas is , where R is the gas constant.
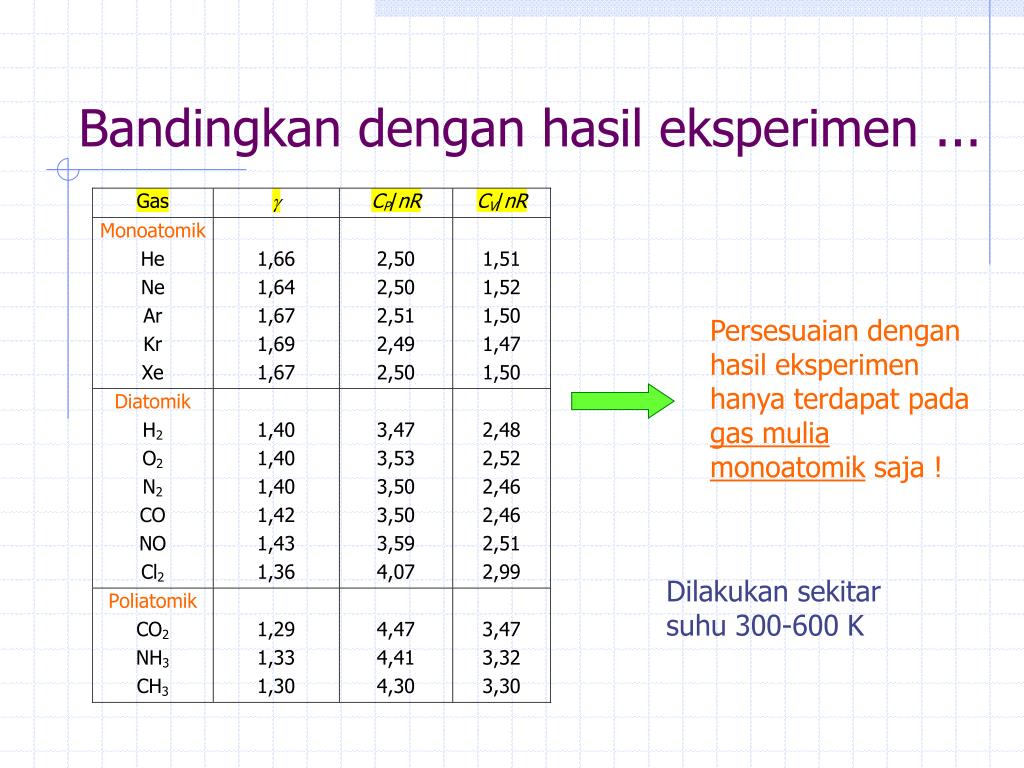
In an adiabatic process, monatomic gases have an idealised γ-factor (Cp/Cv) of 5/3, as opposed to 7/5 for ideal diatomic gases where rotation (but not vibration at room temperature) also contributes. Also, for ideal monatomic gases:[4][5][6]
Gas Ideal Monoatomik Adalah
- the molar heat capacity at constant pressure (Cp) is 5/2 R = 20.8 J K−1 mol−1 (4.97 cal K−1 mol−1).
- the molar heat capacity at constant volume (Cv) is 3/2 R = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1 (2.98 cal K−1 mol−1).

References[edit]
Gas Ideal Monoatomik Memiliki Derajat Kebebasan
- ^'monatomic gas'. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ^Laszlo, Pierre; Schrobilgen, Gary J. (1988-04-01). 'Ein Pionier oder mehrere Pioniere? Die Entdeckung der Edelgas-Verbindungen'. Angewandte Chemie. 100 (4): 495–506. doi:10.1002/ange.19881000406. ISSN1521-3757.
- ^Christe, Karl O. (2001-04-17). 'A Renaissance in Noble Gas Chemistry'. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 40 (8): 1419–1421. doi:10.1002/1521-3773(20010417)40:8<1419::aid-anie1419>3.0.co;2-j. ISSN1521-3773. PMID11317290.
- ^Heat Capacity of an Ideal Gas
- ^Heat Capacity of Ideal Gases
- ^Lecture 3: Thermodynamics of Ideal Gases & Calorimetry[permanent dead link], p. 2
Gas Ideal Monoatomik Bersuhu 57
